The Paleo Diet is rooted in the belief that our genetic makeup is best suited for the foods consumed during the Paleolithic era, before the advent of modern agriculture. Proponents of the diet argue that the agricultural revolution introduced foods like grains, legumes, and dairy that may not align with our bodies’ natural inclinations.
But is the Paleo Diet right for you? That’s the question we’ll tackle. Throughout this article, we’ll walk you through the origins and purpose of the diet, the core components of the Paleo menu, a typical day on the Paleo Diet, the foods to avoid, the potential health benefits, and the criticisms and possible risks associated with this way of eating.
We’ll also guide you in personalizing the Paleo plan to match your individual needs and dietary goals. And, of course, we’ll explore whether consulting with health professionals should be part of your journey towards adopting the Paleo Diet.
So, if you’re ready to embark on a journey back to our ancestral roots and discover if the Paleo Diet is right for you, let’s dive in and explore the wonders of this ancient-inspired way of eating!

Understanding the Paleo Diet
To gain a deeper understanding of the Paleo Diet, it is important to explore its origins and purpose. The Paleo Diet, also known as the caveman diet or Stone Age diet, is based on the idea of consuming foods that were eaten during the Paleolithic era. This diet aims to align our modern eating habits with our genetic makeup, as proponents believe that our bodies are best suited to the foods our ancestors consumed.
The origins of the Paleo Diet can be traced back to the belief that the rise of chronic diseases in the modern world is a result of the agricultural revolution and the introduction of grains, legumes, and dairy into our diets. Advocates of the Paleo Diet argue that our bodies have not evolved enough to properly digest these foods, leading to various health issues. Thus, the Paleo Diet aims to return to a more natural and primitive way of eating, focusing on whole, unprocessed foods.
Origins and Purpose
The Paleo Diet draws inspiration from the time when our ancestors were hunter-gatherers. It is believed that during this era, humans mainly consumed animal protein, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds. This diet was low in carbohydrates and did not include grains, legumes, or dairy products.
The purpose of the Paleo Diet is to restore our eating habits to a more natural state and eliminate foods that are believed to be the cause of modern health problems. Proponents of the diet argue that by eliminating processed foods, grains, and dairy, we can reduce inflammation, stabilize blood sugar levels, improve digestion, and achieve better overall health.
The Paleo Lifestyle
The Paleo Diet is not just about the types of foods consumed but also encompasses a broader lifestyle approach. The Paleo Lifestyle emphasizes the importance of consuming natural, whole foods and avoiding processed foods that are typically high in additives, preservatives, and refined sugars. This lifestyle promotes an active and natural approach to living, incorporating regular exercise and time spent outdoors.

| Paleo Diet | Standard American Diet |
| Emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods | Relies heavily on processed and packaged foods |
| Includes lean meats and fish as sources of protein | Typically high in red and processed meats |
| Encourages the consumption of fruits and vegetables | Often lacks adequate fruit and vegetable intake |
| Avoids grains, legumes, and dairy products | Includes refined grains, legumes, and dairy products |
Note: The table above provides a comparison of the Paleo Diet and the Standard American Diet.
By adopting the Paleo Lifestyle, individuals aim to improve their overall well-being by eating in a way that is more in line with their ancestral heritage. The focus on natural, whole foods and an active lifestyle promotes optimal health and vitality.
What to Eat on a Paleo Diet
It is important to know what foods are allowed and what should be avoided. The core components of the Paleo menu consist of whole, unprocessed foods that were consumed by our ancestors during the Paleolithic era. By focusing on these nutrient-dense foods, you can fuel your body and reap the benefits of this ancestral eating pattern.
Core Components of the Paleo Menu
Meats
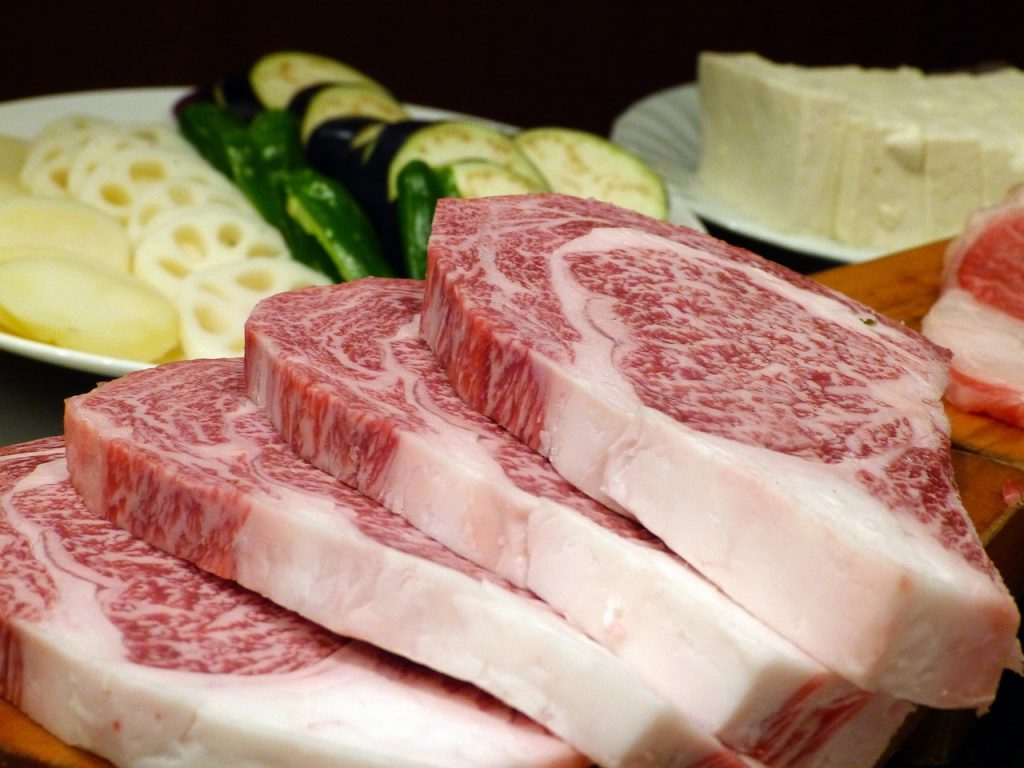

Lean cuts of beef, chicken, turkey, lamb, and game meats are all Paleo-approved sources of protein. Look for grass-fed and pasture-raised options whenever possible.
Fish and Seafood
Include fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Other seafood such as shrimp, scallops, and shellfish are also great choices.
Vegetables
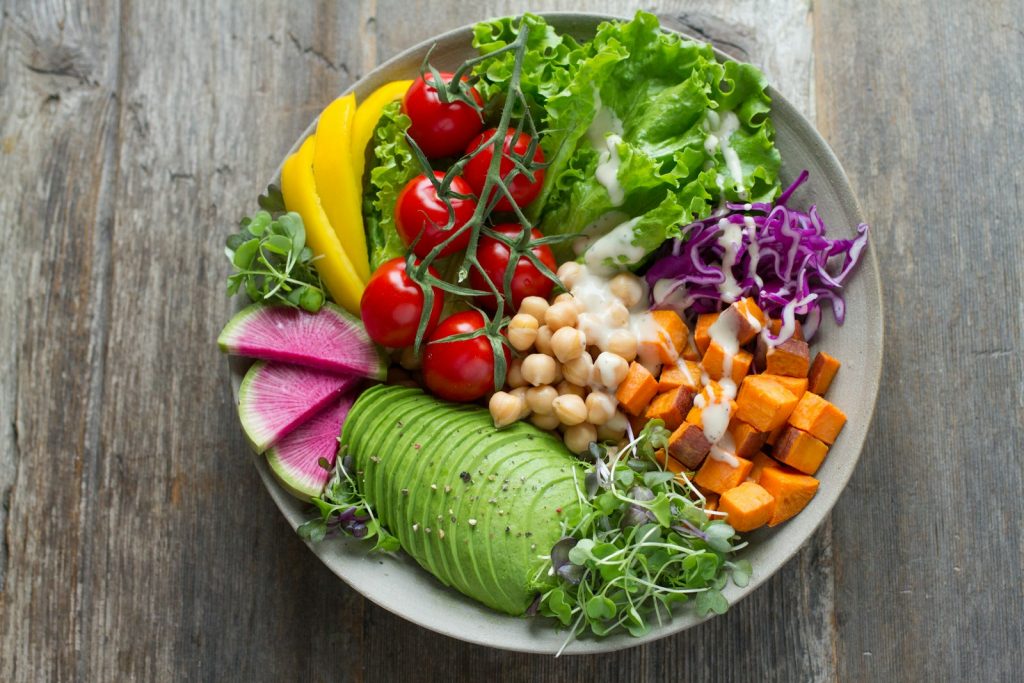

Load up your plate with a variety of colorful vegetables like leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, carrots, and bell peppers. These provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
Fruits

Enjoy a wide range of fruits, including berries, apples, oranges, bananas, and melons. These provide natural sweetness and valuable antioxidants.
Nuts and Seeds

Incorporate healthy fats and proteins by including almonds, walnuts, cashews, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and pumpkin seeds in your diet
By focusing on these core components, you can create a well-balanced Paleo meal plan that nourishes your body and supports optimal health.
A Day in the Life on the Paleo Diet
Living a Paleo lifestyle means embracing a whole new way of eating that focuses on natural, unprocessed foods. In this section, we will take a closer look at what a typical day on the Paleo Diet looks like, how to craft a Paleo meal plan, and how to adapt to the Paleo lifestyle.
Crafting Your Paleo Meal Plan
One of the keys to success on the Paleo Diet is planning and preparing your meals in advance. By creating a Paleo meal plan, you can ensure that you’re getting a balanced and nutritious diet that aligns with the principles of the Paleo lifestyle. Here are some tips and suggestions to help you craft your Paleo meal plan:
- Start with the basics: Include plenty of lean meats, fish, vegetables, fruits, nuts, and seeds in your meal plan. These are the core components of the Paleo menu and should form the foundation of your meals.
- Vary your protein sources: Experiment with different types of meats and fish to keep your meals interesting. Incorporate poultry, beef, pork, seafood, and game meats into your weekly rotation.
- Load up on vegetables: Fill your plate with a variety of colourful vegetables to ensure you’re getting a wide range of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Focus on non-starchy vegetables like leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, peppers, and mushrooms.
- Include healthy fats: Don’t shy away from fats on the Paleo Diet. Include sources like avocados, olive oil, coconut oil, and nuts to provide your body with essential fatty acids.
- Plan your snacks: Incorporate Paleo-friendly snacks into your meal plan to keep you satisfied throughout the day. Consider options like hard-boiled eggs, sliced veggies with guacamole, or homemade Paleo-friendly protein bars.
Adapting to the Paleo Lifestyle
Adapting to the Paleo lifestyle involves more than just changing your diet. It requires making adjustments to your daily routines and navigating social situations that may not align with the Paleo principles. Here are some tips to help you adapt to the Paleo lifestyle:
- Find suitable substitutes: Identify suitable substitutes for non-Paleo foods to satisfy cravings and maintain a balanced diet. For example, replace pasta with zucchini noodles or use cauliflower rice instead of traditional rice.
- Focus on real, whole foods: Embrace the Paleo philosophy of eating real, whole foods and avoiding processed foods as much as possible. Stick to the perimeter of the grocery store where fresh produce, meats, and seafood are typically located.
- Be prepared when eating out: Research restaurant menus in advance and look for Paleo-friendly options. When dining out, focus on simple grilled meats, seafood, and vegetable dishes. Don’t be afraid to ask questions or make modifications to your order to ensure it aligns with the Paleo Diet.
- Seek support: Connect with others who follow the Paleo Diet for support and inspiration. Join online communities or local groups to share recipes, tips, and success stories. Having a support network can make the transition to the Paleo lifestyle easier.
| A Day on the Paleo Diet | Meal | Sample Foods |
| Breakfast | Scrambled Eggs with Vegetables | Eggs, spinach, tomatoes, onions |
| Lunch | Grilled Chicken Salad | Grilled chicken, mixed greens, cucumber, avocado |
| Afternoon Snack | Carrot Sticks with Almond Butter | Carrots, almond butter |
| Dinner | Grilled Salmon with Roasted Vegetables | Salmon, broccoli, cauliflower, bell peppers |
| Evening Snack | Apple Slices with Almond Butter | Apple, almond butter |
Remember, this is just an example, and your Paleo meal plan can be customized to suit your preferences and dietary needs. Experiment with different recipes and ingredients to find what works best for you.
What’s NOT on the Menu

The Paleo Diet is known for its strict guidelines on food choices, emphasizing a return to our ancestors’ way of eating. Many food groups that are common in modern diets are excluded from the Paleo menu, including grains, legumes, dairy, refined sugar, and processed foods. By eliminating these foods, the Paleo Diet aims to promote a more natural and nutrient-dense approach to eating.
Grains
This includes wheat, rice, corn, and oats. These foods are avoided because they contain anti-nutrients, such as lectins and phytates, which can interfere with nutrient absorption and digestion.
Legumes
Beans, lentils, soybeans, and peanuts are among the legumes excluded from the Paleo Diet. These foods can be high in lectins and may cause digestive issues for some individuals.
Dairy
Milk, cheese, yogurt, and other dairy products are not allowed on the Paleo Diet. The reasoning behind this exclusion is that the consumption of dairy is a relatively recent development in human history and may be associated with digestive issues and inflammation.
Refined Sugar
All forms of refined sugar, including white sugar, brown sugar, and high-fructose corn syrup, are excluded from the Paleo Diet. Instead, natural sweeteners like honey, maple syrup, and coconut sugar are encouraged in moderation.
Processed Foods
Processed foods, such as packaged snacks, fast food, and prepackaged meals, are not compatible with the Paleo Diet. These foods often contain additives, preservatives, and unhealthy fats that are not in line with the natural and whole-food approach of the diet.
While the exclusion of these food groups is a key aspect of the Paleo Diet, there is ongoing debate regarding some of these exclusions. One area of controversy is the role of carbs and dairy in the Paleo Diet:
The Debate Around Carbs and Dairy
Carbohydrates and dairy products have been staples in many traditional diets, but they are excluded from the Paleo Diet. Critics argue that excluding these food groups may result in nutrient deficiencies and limit dietary variety, while proponents believe that the exclusion can lead to improved health.
When it comes to carbohydrates, it is important to note that the Paleo Diet does not encourage the consumption of refined carbohydrates found in processed foods. Instead, the focus is on obtaining carbohydrates from fruits, vegetables, and tubers. These sources provide a range of vitamins, minerals, and fiber while minimizing the negative effects associated with refined carbs.
In terms of dairy, the exclusion is based on the belief that lactose intolerance, the inability to digest lactose found in milk, is common in many populations. Additionally, dairy products may contain hormones and antibiotics that could be detrimental to health. However, some individuals can tolerate dairy products well and may benefit from their nutrient content.
Complete the table below with relevant data on the exclusions in the Paleo Diet:
| Excluded Food Group | Reason for Exclusion |
| Grains | Contain anti-nutrients that may interfere with nutrient absorption and digestion |
| Legumes | Can be high in lectins and may cause digestive issues |
| Dairy | Relatively recent development in human history, potential for digestive issues and inflammation |
| Refined Sugar | Highly processed and lacks nutritional value |
| Processed Foods | Contain additives, preservatives, and unhealthy fats |
It’s important to note that individual dietary needs and preferences may vary, and some individuals may choose to make modifications to the Paleo Diet to better suit their needs. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance and ensure any adaptations to the diet are done safely and appropriately.
Evaluating the Paleo Diet

In this section, we will examine the Paleo Diet from a health perspective, evaluating its potential benefits, possible risks, and effectiveness in achieving desired health outcomes.
Health Benefits
The Paleo Diet is often associated with several health benefits. These include:
- Weight loss: The emphasis on whole, unprocessed foods and the exclusion of refined sugar and processed foods can support weight loss efforts.
- Improved blood sugar and lipid profiles: By eliminating added sugars and focusing on nutrient-dense foods, the Paleo Diet may help regulate blood sugar levels and improve lipid profiles.
- Increased nutrient intake: With an emphasis on fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, the Paleo Diet can provide a wide range of essential nutrients.
Possible Risks and Criticisms
While the Paleo Diet may offer potential benefits, it is essential to consider possible risks and criticisms as well. These include:
- Nutrient deficiencies: Eliminating entire food groups like grains and dairy may lead to potential nutrient deficiencies if not properly balanced and supplemented.
- High saturated fat intake: The reliance on red meat in the Paleo Diet may result in a higher intake of saturated fats, which can have implications for cardiovascular health.
- Exclusion of certain food groups: Some critics argue that eliminating entire food groups may limit dietary variety and potentially overlook important nutrients.
Paleo Diet Effectiveness
The effectiveness of the Paleo Diet in achieving desired health outcomes is a topic of discussion among researchers and experts. While some studies suggest that the diet can lead to weight loss and improvements in certain health markers, others question its long-term sustainability and potential drawbacks.
“As with any diet, the effectiveness of the Paleo Diet can vary depending on individual adherence, dietary preferences, and overall lifestyle factors. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine if the Paleo Diet is suitable for your specific needs and goals.”
By considering the potential health benefits, possible risks, and effectiveness of the Paleo Diet, individuals can make informed decisions about whether it aligns with their personal dietary goals and health needs.
Making It Work for You
It is important to personalize your Paleo plan based on your dietary goals, health requirements, and food preferences. By customizing the Paleo Diet, you can make it more sustainable and enjoyable for yourself.
Personalizing Your Paleo Plan:
When personalizing your Paleo plan, consider the following factors:
- Your Dietary Goals: Determine what specific goals you want to achieve with the Paleo Diet. It could be weight loss, improved energy levels, or better overall health. Understanding your goals will help you focus on the right strategies for personalizing your plan.
- Your Health Needs: Take into account any specific health conditions or dietary restrictions you may have. Consult with a healthcare professional, such as a registered dietitian, to ensure that your personalized Paleo plan meets your nutritional requirements.
- Your Food Preferences: Consider your taste preferences and the foods you enjoy the most. The Paleo Diet offers a wide variety of options, so you can customize your plan to include the foods that you find most enjoyable.
By personalizing your Paleo plan, you can create a sustainable and enjoyable eating pattern that aligns with your goals and preferences.
Addressing Common Questions and Concerns:
Here are answers to some common questions and concerns about the Paleo Diet:
- Can I follow a vegetarian or vegan Paleo Diet? While the traditional Paleo Diet includes animal-based foods, you can modify it to fit a vegetarian or vegan lifestyle. Focus on including plant-based protein sources such as tofu, tempeh, and legumes while avoiding grains and dairy.
- Will I get enough nutrients on the Paleo Diet? With careful planning and food choices, the Paleo Diet can provide all the necessary nutrients. Ensure that you include a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, meats, fish, nuts, and seeds to meet your nutritional needs.
- Is the Paleo Diet suitable for everyone? The Paleo Diet may not be suitable for everyone, especially individuals with certain health conditions or dietary restrictions. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any significant dietary changes.
- How do I deal with cravings for non-Paleo foods? Cravings for non-Paleo foods are common, especially during the initial transition. Find suitable Paleo alternatives for your favorite non-Paleo foods, experiment with new recipes, and focus on the delicious and nutritious foods that you can enjoy on the Paleo Diet.
By addressing these common questions and concerns, you can navigate the Paleo Diet more confidently and make informed decisions about your dietary choices.
Is the Paleo Diet Right for You?
In order to determine if the Paleo Diet is suitable for you, it is important to consider your dietary goals, health needs, and lifestyle preferences. While the Paleo Diet has gained popularity for its potential health benefits, it may not be the best fit for everyone.
Considering Your Dietary Goals and Health Needs
Before embarking on any significant dietary changes, it is essential to assess your specific dietary goals and health needs. Ask yourself what you hope to achieve with the Paleo Diet. Are you looking to lose weight, improve your overall well-being, or manage a specific health condition? Understanding your goals will help determine if the Paleo Diet aligns with your objectives.
Additionally, take into account any dietary restrictions or preferences you may have. Some individuals may find it challenging to adhere to the restrictions imposed by the Paleo Diet, such as the exclusion of grains, legumes, and dairy. Consider whether you are willing and able to make these adjustments to your eating habits.
Consulting with Health Professionals
Consulting with health professionals, such as registered dietitians or doctors, is highly recommended before starting any new diet plan. They can provide valuable insights and guidance based on your individual health profile and dietary needs. A healthcare professional can help determine if the Paleo Diet is appropriate for your specific circumstances and advise on any adjustments or modifications that may be necessary.
During your consultation, be prepared to discuss your dietary goals, health history, and any existing medical conditions or concerns. A healthcare professional can assess the suitability of the Paleo Diet in relation to your unique circumstances and provide personalized recommendations.
Taking the time to consult with health professionals ensures that you make informed decisions about your dietary choices and receive the support and guidance needed to follow the Paleo Diet safely and effectively.
Pros and Cons of the Paleo Diet
| Pros | Cons |
| Emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods Potential for weight loss Possible improvements in blood sugar and lipid profiles Increased intake of nutrients | Excludes entire food groups (grains, legumes, dairy) Potential for nutrient deficiencies High saturated fat intake Strict dietary restrictions may be challenging for some |
Conclusion
After exploring the key aspects of the Paleo Diet, it’s time to wrap up our discussion. The Paleo Diet, also known as the caveman or Stone Age diet, is based on the belief that our modern chronic diseases stem from the introducing of grains, legumes, and dairy during the agricultural revolution. By focusing on natural, whole foods and eliminating processed options, the Paleo Diet aims to align with our genetic makeup.
Ultimately, whether the Paleo Diet is right for you is a personal decision. It’s essential to consider your dietary goals, health needs, and lifestyle preferences. Consulting with a health professional, such as a registered dietitian or doctor, can help you navigate these considerations and make well-informed choices.
Remember, nutrition is not one-size-fits-all, and it’s crucial to personalize your approach to match your individual needs. Whether you choose to follow the Paleo Diet or explore other dietary paths, prioritize a balanced and well-rounded approach. With the right knowledge and informed decision-making, you can take control of your health and make choices that serve you best.


